Building and maintaining healthy bones and heart is one of Calcium's most common functions in the human body.
But there is so much more to this mighty mineral.
All cells need calcium in order to maintain optimal health. Besides taking care of our teeth and bones, small amounts of calcium are dispersed in the blood and cells as ions. Ionic calcium is a type of calcium in the blood with a weak bonding force, or in other words, not attached to proteins. This ionic calcium is important for balancing our body, a process known as homeostasis. Calcium that lives inside the blood is responsible for critical functions such as muscle contractions, blood vessel contractions, and nerve signals. When there is a deficiency of ionic calcium, chronic diseases controlled by hormones may develop.
Read on to discover what happens to your body when you have a calcium deficiency.
CALCIUM DEFICIENCY SYMPTOMS
Before we dive into what can happen to your body as a result of a calcium deficiency, let’s take a look at calcium deficiency symptoms to look out for:
CALCIUM DEFICIENCY HEALTH CONDITIONS
As mentioned above, there are a variety of health conditions that can develop from a lack of calcium in the body. The following are four specific issues associated with calcium deficiency, each of which is explained in more detail below.
Calcium deficiency and osteoporosis:
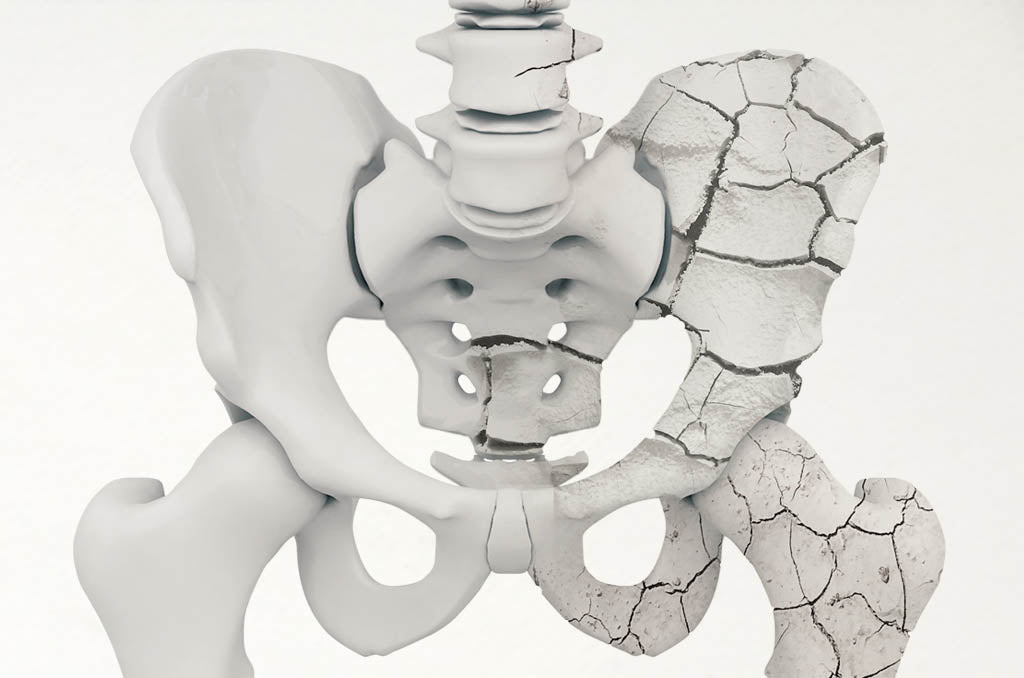
Osteoporosis occurs when bone mass decreases or bone structure changes and can be caused by a lifelong lack of calcium. It's a health condition that progressively weakens bone strength which in turn increases the risk of fractures.
A person with osteoporosis is at high risk for broken bones, especially in the wrist, hip, and spine. In addition to causing ongoing pain and disability, they can also reduce one's quality of life and cause them to lose independence.
Cleveland Clinic states that people with low calcium intake are more likely to develop osteoporosis.
Those who suffer from osteoporosis can experience fractures of the spine's vertebrae. Consequently, these spine areas weaken and collapse, resulting in pain, difficulty with movement, and gradual deformity. In severe cases a curvature of the upper back can develop.
An unhealthy calcium intake can diminish bone density, cause early bone loss, and increase fracture risk.
Calcium deficiency and Osteopenia:
The definition of osteopenia is low bone density, but not a level that qualifies as osteoporosis.
Having low calcium levels can make bones brittle and prone to injury, since the body diverts calcium from the bones. It is possible to suffer osteopenia, a decrease in bone mineral density, as a result of having too little calcium over time.
A person with less bone to lose could be more likely to get osteoporosis if they lose bone in the future. In addition, people with low bone density are more prone to breaking a bone.
When calcium is deficient, osteoporosis and other complications can develop slowly over years; however, it’s never too early to keep an eye out for symptoms of osteoporosis.
Calcium deficiency and heart disease:
Getting enough calcium in your diet, whether through good food or supplements, is crucial to your heart's health.
According to CDC, Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States with men at a higher risk of heart attacks than women. As a matter of fact, younger men are more likely to suffer from a heart attack earlier in life than younger women. Despite diet, exercise, and smoking being influencing factors, calcium deficiency can also lead to this life-threatening condition.
Research states that having too little calcium has been linked with heart failure, low blood pressure (hypotension) and life-threatening rhythm disorders of the heart.
Calcium deficiency disease (hypocalcemia):
A healthy body requires calcium to function properly. The level of calcium in your blood is controlled by your hormones and Hypocalcemia occurs when your blood calcium level is too low.
Web MD states that Hypocalcemia occurs when your bones produce too little calcium or too much calcium leaves your body when you urinate. This could be caused by certain genetic factors or a calcium deficiency. Low calcium levels or disorders that impede your body's ability to absorb calcium can result in hypocalcemia.
HOW TO PREVENT CALCIUM DEFICIENCIES
The health of your bones depends on a good diet packed with Calcium and regular exercise. However, with the depreciation of food quality, finding this essential mineral in food can be tricky.
The recommended daily intake of calcium is 1,000 mg for women age 50 and younger and men after 70 and younger or 1,200 mg for women over 50 and men over 70.
Calcium supplements may be beneficial if you are unable to get enough calcium through your diet. That’s exactly what Marah Natural’s SAC Formulation Technology has been designed for!
SIGMA ANTI-BONDING CALCIUM CARBONATE
SAC (Sigma Anti-bonding Calcium Carbonate) is the only true ionic calcium delivery system that provides calcium in a free ionic state, which is the only physiologically active form of calcium in our body. Normally, calcium from diet and supplements enters our body in the protein-bound form and therefore, cannot trigger the same physiological responses as SAC. Resolving calcium deficiency better than protein-bound calcium, SAC triggers ionic-calcium-sensitive physiological responses that counteract the root cause of diseases and brings natural healing reactions of our body from cellular to the systemic level.
"SAC is the world's first safe calcium-ion delivery system administered directly into our body in oral form. SAC triggers healing mechanisms no other calcium supplementation can achieve"
See our collection of ionic calcium: